Why DVT Ultrasound Scans are Essential for Accurate Diagnosis
Introduction:
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is a serious medical condition that occurs when a blood clot forms in a deep vein, often in the legs. It can lead to severe complications if left untreated, including pulmonary embolism, which can be fatal. In order to accurately diagnose DVT, healthcare professionals rely on various imaging techniques, with ultrasound playing a crucial role. This article will explore why DVT ultrasound scans are essential for accurate diagnosis, highlighting their benefits, the procedure, and their role in preventing potential complications.
Understanding DVT and Its Risks:
Before delving into the importance of ultrasound scans, it is important to grasp the nature of DVT and its associated risks. DVT primarily affects the deep veins in the legs, where blood flow is slower compared to the arteries. This sluggish blood flow, combined with certain risk factors such as prolonged immobility, obesity, and family history, increases the likelihood of blood clot formation. If a clot dislodges and travels to the lungs, it can cause a life-threatening pulmonary embolism.
The Role of Ultrasound in DVT Diagnosis:
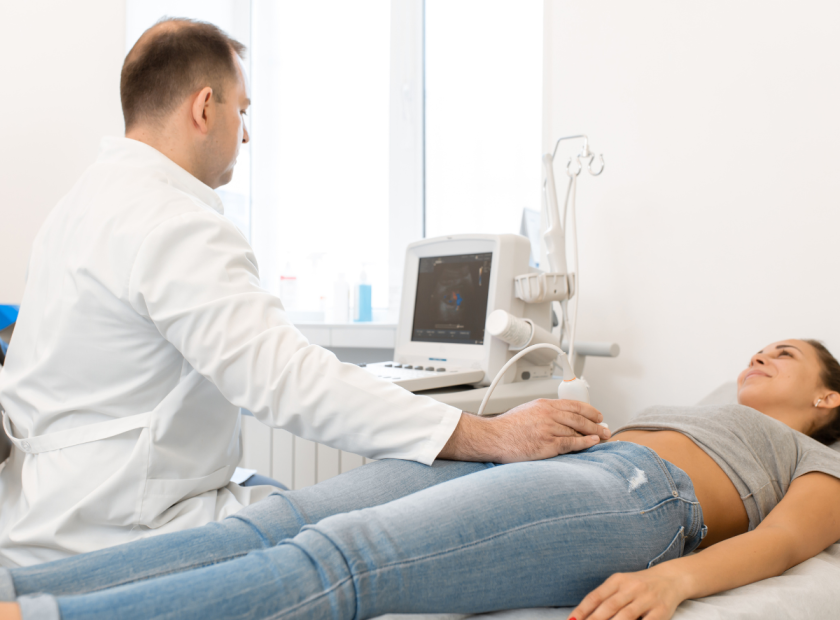
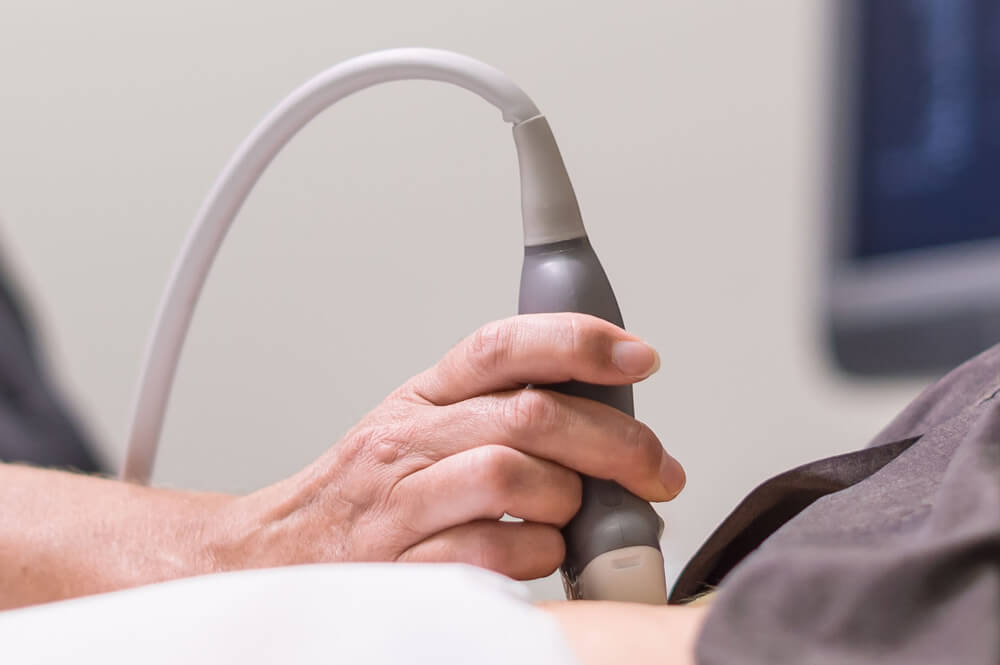
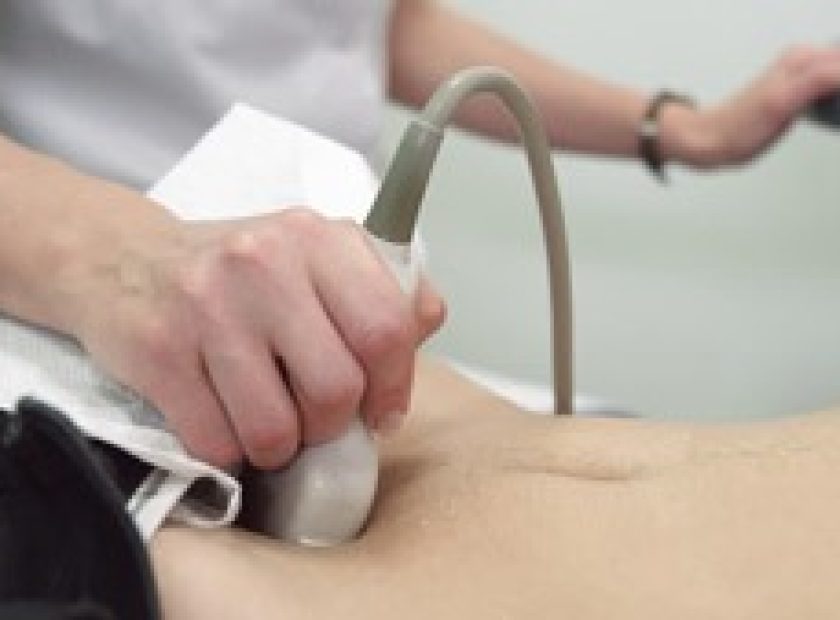
Ultrasound is a non-invasive imaging technique that utilizes sound waves to produce real-time images of the body’s internal structures. In the case of DVT, ultrasound plays a vital role in diagnosing the condition accurately. It allows healthcare professionals to visualize the veins, identify blood clots, and assess their extent and location. Unlike other imaging methods like magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) scans, ultrasound does not involve ionizing radiation, making it safer for patients.
Advantages of DVT Ultrasound Scans:
-
Accuracy: DVT ultrasound scans are known for their high accuracy in detecting blood clots. They provide real-time images, enabling immediate visual confirmation of DVT, thereby facilitating prompt treatment initiation.
-
Safety: As mentioned earlier, ultrasound scans do not expose the patient to any harmful radiation. This makes it a safer option, particularly for pregnant women, children, and individuals who require repeated scans.
-
Non-invasiveness: Unlike other diagnostic procedures, such as venography, which involves injecting a contrast dye into the veins, ultrasound scans are non-invasive. It involves the use of a handheld device or transducer that is gently moved over the skin.
-
Cost-effectiveness: DVT ultrasound scans are generally more affordable compared to other imaging techniques, making them accessible to a wider range of patients. This affordability allows for more frequent monitoring of patients at risk and facilitates early detection.
The DVT Ultrasound Procedure:
During a DVT ultrasound scan, a healthcare professional applies a gel to the skin over the area being examined. The transducer, which emits sound waves, is then placed on the gel-coated skin. The healthcare professional moves the transducer along the veins, capturing images that are displayed on a monitor in real-time. By analyzing the images, they can identify any blood clots present and assess their severity. The procedure is painless and typically takes less than 30 minutes to complete.
Preventing Complications and Ensuring Proper Treatment:
Early and accurate diagnosis of DVT through ultrasound scans is crucial for initiating appropriate treatment promptly. Anticoagulant medications, also known as blood thinners, are commonly prescribed to prevent further clot formation and reduce the risk of pulmonary embolism. Depending on the severity of the clot, more aggressive treatments like thrombolytic therapy may be considered.
Conclusion:
DVT ultrasound scans play a fundamental role in accurately diagnosing DVT, allowing for timely treatment and reducing the risk of life-threatening complications. The advantages of ultrasound, including its safety, non-invasiveness, cost-effectiveness, and high accuracy, make it the preferred diagnostic option for healthcare professionals. By utilizing ultrasound technology, physicians can closely monitor patients at risk, detect DVT at its earliest stages, and provide appropriate care.