Understanding the Results: Interpretation of Thyroid Ultrasound Scans
Thyroid Ultrasound Results Explained
Thorough Research on Thyroid Ultrasound Scan Interpretation:
To provide you with accurate and up-to-date information, we have conducted extensive research on thyroid ultrasound scans, consulting reputable medical literature, expert opinions, and clinical studies. Our aim is to present a well-rounded understanding of this topic, ensuring that you gain insights from a variety of reputable sources. The following sections will delve into common findings and their implications, ultimately providing you with a guide and explanation on the interpretation of Thyroid results and Thyroid ultrasound scan reports.
If you would like to know more about the Thyroid functions and the role it has in maintaining your health, we have specialist GPs and practitioners to guide and advise you.
Thyroid Disease Test Results:
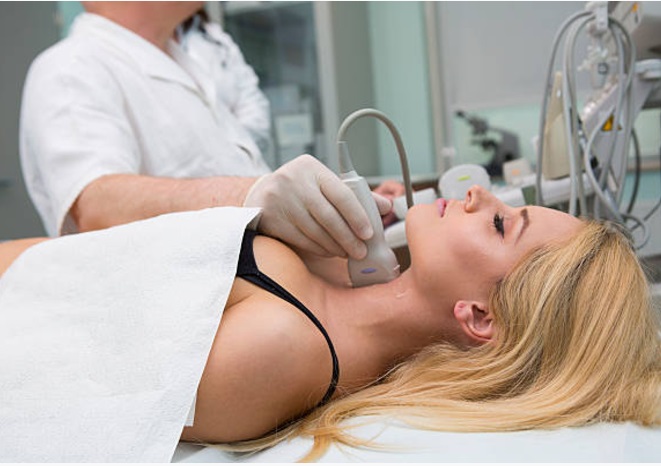
Thyroid ultrasound scans typically evaluate the size, shape, texture, and vascularity of the thyroid gland, aiding in the identification of potential abnormalities. Here, your will find thyroid ultrasound results explained and insight into the most common findings and their interpretations:
Thyroid Nodules: Thyroid nodules are small, solid or fluid-filled lumps that can be detected through ultrasound scans. Nodule characteristics such as size, shape, echogenicity (brightness on the scan), and vascularity are crucial in determining their nature. While most nodules are benign, further evaluation and monitoring are often necessary to rule out malignancy.
Thyroid Enlargement (Goiter): Goiter refers to an enlarged thyroid gland, which can be detected through ultrasound imaging. The scan will assess the size, symmetry, and structural abnormalities of the gland. Goiter may indicate an underlying thyroid disorder, such as Graves’ disease or Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, and further investigation is crucial to determine the underlying cause.
Thyroid Cysts: Thyroid cysts are fluid-filled sacs within the thyroid gland. Their appearance on ultrasound scans can greatly vary, ranging from simple cysts (benign) to complex cystic nodules. Close monitoring and evaluation are necessary, as complex cystic nodules may require further investigation to rule out malignancy.
Hypoechoic/Hyperechoic Lesions: Lesions that appear hypoechoic (darker) or hyperechoic (brighter) than the surrounding thyroid tissue may indicate various conditions. Hypoechoic lesions are often associated with thyroid cancer, while hyperechoic lesions can be a result of inflammation or fat deposition. Accurate characterization and follow-up are crucial to determine the appropriate course of action.
Thyroiditis: Thyroiditis refers to inflammation of the thyroid gland, which can be categorised into different types, including Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and subacute thyroiditis. Ultrasound scans can help identify the characteristic features of thyroiditis, such as gland enlargement, altered echogenicity, and blood flow changes. Prompt diagnosis and management can help alleviate symptoms and prevent complications.
Thyroid Ultrasounds Results Explained
Interpreting thyroid ultrasound scan results is a complex process that requires expertise and advanced knowledge. By understanding the significance of different findings, one can effectively navigate through potential diagnoses and treatment options. We hope this article has provided you with valuable insights into interpreting thyroid ultrasound scans.
If you require a consultation on a thyroid concern, we can provide telephone and face to face consultations as well as the specialists to perform ultrasound with advanced imaging technology.
For more general information on the benefits of ultrasound we have extensive online resources available to you.