The Ultimate Comparison: Liver Ultrasound vs. CT Scan
In the world of medical diagnostics, liver ultrasounds and CT scans play vital roles in assessing liver health and identifying potential conditions. While both methods offer valuable insights, they differ in terms of functionality, detail, and specific clinical requirements. In this extensive comparison, we will delve into the distinctive features of liver ultrasounds and CT scans, helping you understand their benefits, limitations, and ultimately, which option is best suited for your unique medical needs.
Understanding Liver Ultrasounds:
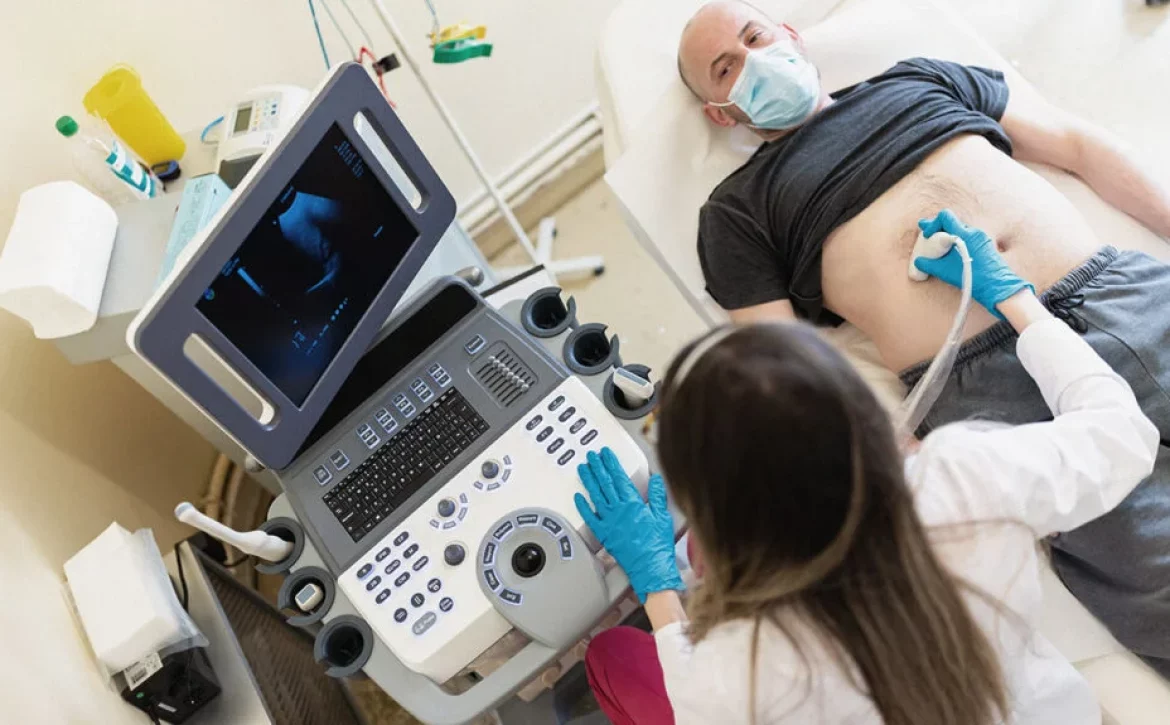
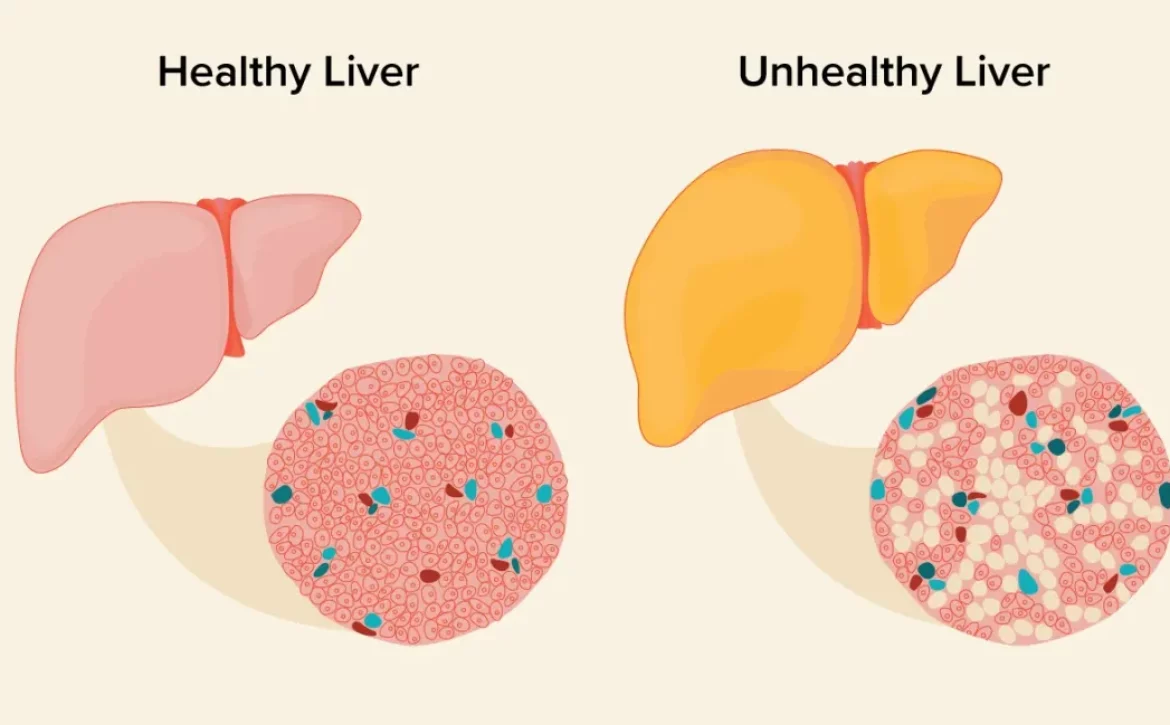
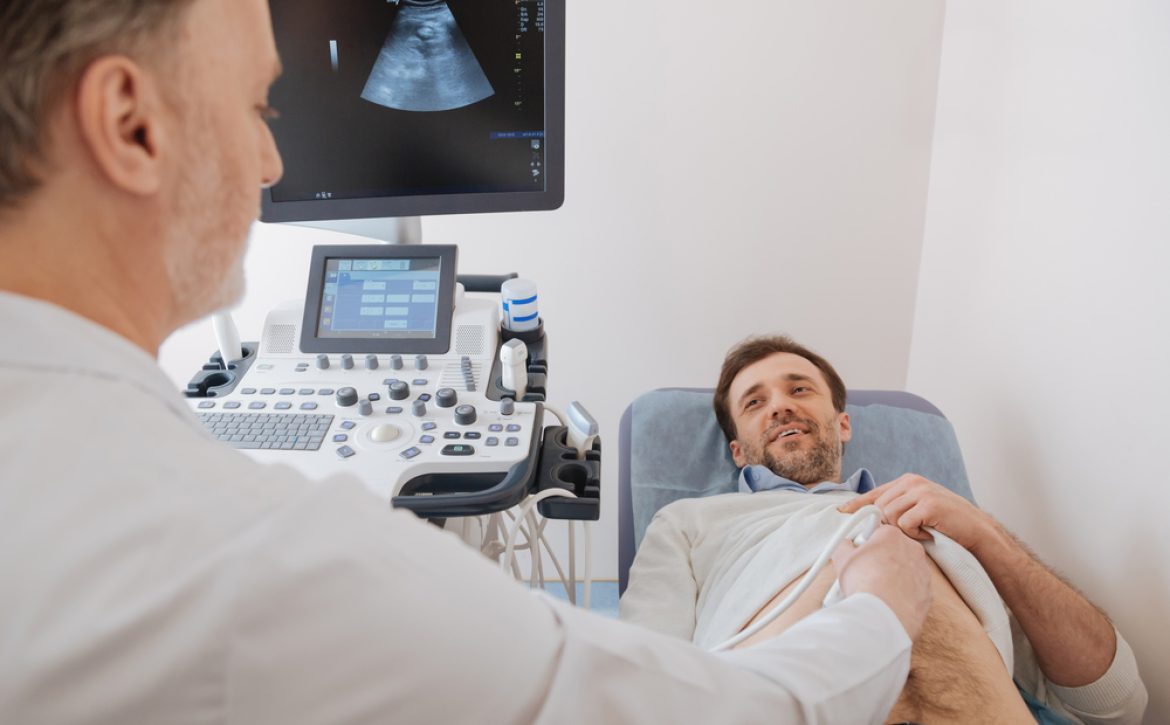
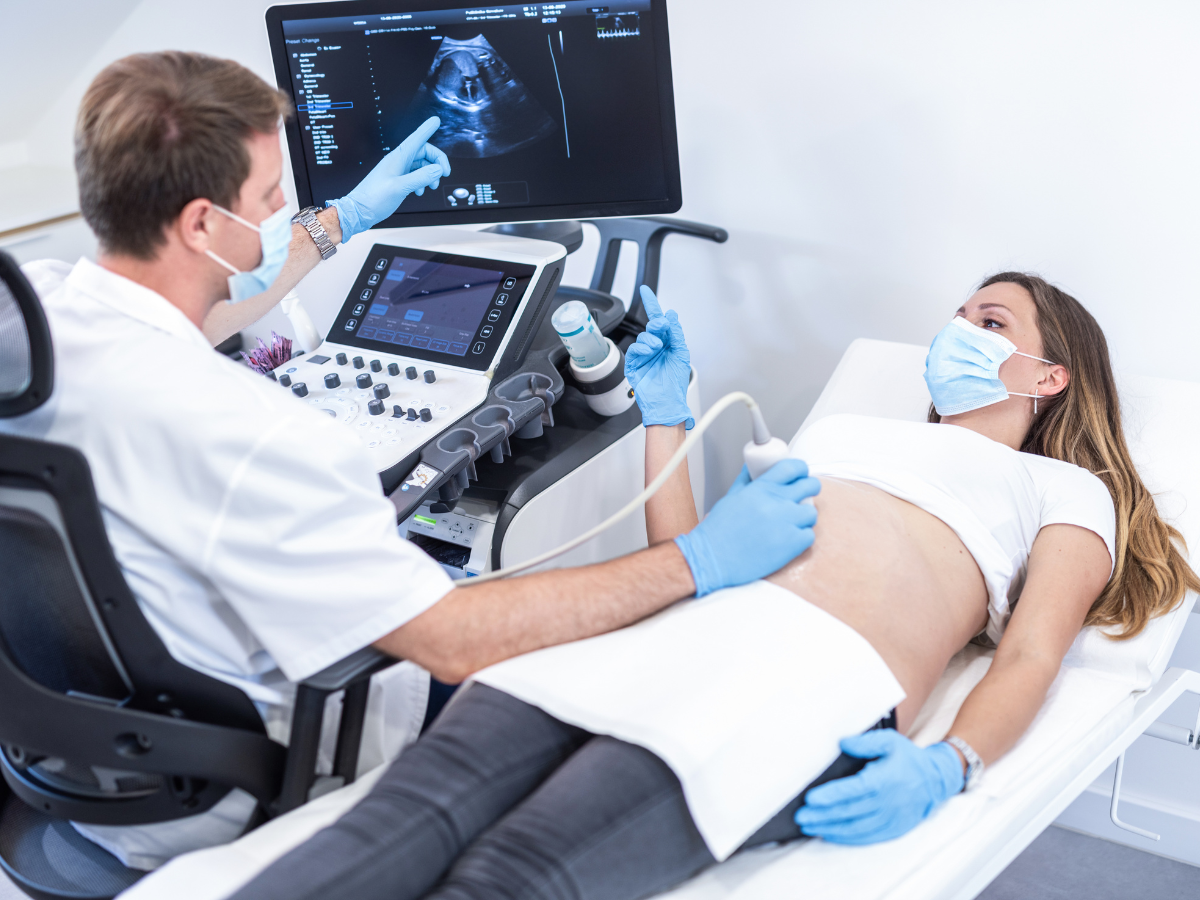
A liver ultrasound, also known as sonography, utilizes sound waves to produce detailed images of the liver. This non-invasive procedure allows medical professionals to examine the liver’s structure, size, and general condition. It is particularly effective in identifying liver masses, cysts, and abnormal growths. The absence of radiation makes it a safe option for regular screening and monitoring of liver health.
Despite its advantages, liver ultrasounds have limitations. The quality of images can be impacted by factors such as the patient’s body habitus and bowel gas interference, sometimes hindering accurate diagnosis. Additionally, liver ultrasounds may not provide detailed information on liver blood flow and functionality. However, when used in conjunction with other diagnostic tools, they can offer complementary insights into liver health.
Unveiling the Power of CT Scans:
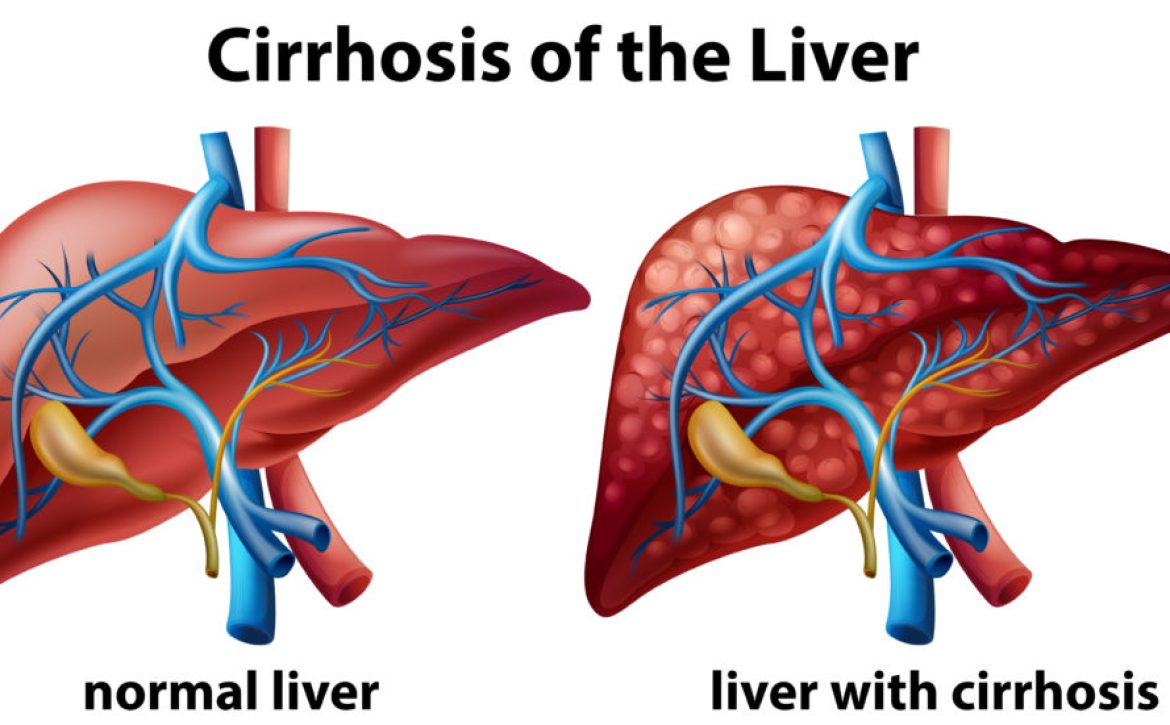
A CT scan, short for computed tomography, employs X-ray technology to capture cross-sectional images of the liver. This imaging modality provides detailed visualizations of the liver’s internal structures, blood vessels, and potential abnormalities. CT scans offer a higher level of precision compared to ultrasounds, enabling radiologists to detect minute lesions, tumors, and even signs of cirrhosis or hepatocellular carcinoma.
While CT scans provide a comprehensive assessment of the liver, they involve exposure to ionizing radiation. Consequently, precautions must be taken, particularly for patients who require frequent imaging or those with pre-existing radiation exposure concerns. CT scans are commonly used for investigating complex liver conditions and assisting in treatment planning.
Comparing Benefits and Limitations:
To determine the most suitable diagnostic tool for your liver assessment, let’s compare the benefits and limitations of liver ultrasounds and CT scans:
- Benefits of Liver Ultrasounds:
- Non-invasive, safe, and painless procedure
- Able to identify liver masses, cysts, and abnormalities
- Suitable for regular screenings and monitoring
- No exposure to ionizing radiation
- Limitations of Liver Ultrasounds:
- Quality of images influenced by body habitus and bowel gas
- Limited information on blood flow and liver functionality
- Benefits of CT Scans:
- Excellent visualization of internal liver structures and blood vessels
- High precision in detecting small lesions and tumors
- Useful for complex liver conditions and treatment planning
- Limitations of CT Scans:
- Involves exposure to ionizing radiation
- Not recommended for frequent imaging or concerns with radiation exposure
Choosing the Right Diagnostic Tool:
The choice between a liver ultrasound and a CT scan relies on various factors, including the patient’s symptoms, medical history, and the level of detail required for diagnosis. For routine check-ups and initial screenings, liver ultrasounds are often the preferred option due to their safety, accessibility, and ability to detect major abnormalities. Conversely, if further investigation is necessary or if complex liver conditions are suspected, CT scans may provide the precision and visualization required for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
Conclusion:
In the realm of liver health diagnostics, both liver ultrasounds and CT scans are indispensable tools. While ultrasounds offer a safe, non-invasive screening method, CT scans deliver detailed visualizations, aiding in the detection of smaller lesions and complex conditions. By understanding the benefits and limitations of each method, medical professionals can make informed decisions about the appropriate diagnostic approach for patients.