Understanding Liver Cirrhosis: Causes, Symptoms, and Management
At our ultrasound clinic in London, we recognize the importance of educating our community about various liver conditions. Liver cirrhosis is a serious health concern that requires awareness, understanding, and timely management. In this article, we will delve into the causes, symptoms, and effective strategies for managing liver cirrhosis.
What is Liver Cirrhosis?
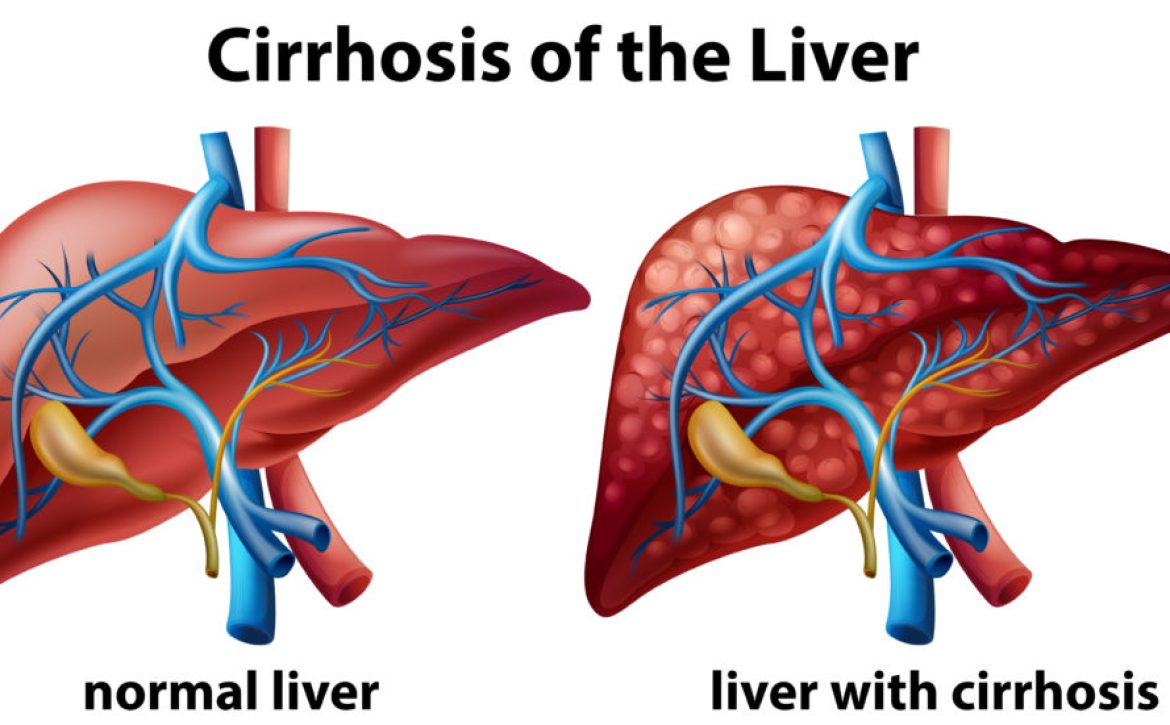
Liver cirrhosis is a progressive and irreversible condition in which healthy liver tissue is replaced by scar tissue. This scarring affects the liver’s normal structure and function, impairing its ability to perform vital tasks such as detoxification, protein synthesis, and bile production. If left untreated, cirrhosis can lead to severe complications, including liver failure.
Causes of Liver Cirrhosis:
Chronic Alcohol Abuse: Prolonged and excessive alcohol consumption is a leading cause of cirrhosis. Alcohol can directly damage liver cells and promote the accumulation of scar tissue.
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): NAFLD, often associated with obesity and metabolic syndrome, involves the accumulation of fat in the liver. Over time, this can progress to cirrhosis.
Autoimmune Hepatitis: In this condition, the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks liver cells, causing inflammation and potential cirrhosis.
Genetic Disorders: Certain genetic conditions, such as hemochromatosis (excess iron accumulation) and Wilson’s disease (copper buildup), can contribute to cirrhosis.
Biliary Diseases: Conditions that affect the bile ducts, such as primary biliary cirrhosis and primary sclerosing cholangitis, can lead to cirrhosis.
Symptoms of Liver Cirrhosis:
In its early stages, cirrhosis may not cause noticeable symptoms. As the disease progresses, the following signs and symptoms may emerge:
Fatigue and weakness.
Loss of appetite.
Unexplained weight loss.
Nausea and vomiting.
Abdominal pain and discomfort.
Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes).
Swelling in the legs and abdomen.
Itchy skin.
Importance of Early Detection:
Early detection and intervention are crucial for managing cirrhosis and preventing further liver damage. As a reputable ultrasound clinic in London, we offer advanced imaging techniques that aid in the early diagnosis and monitoring of liver health.
Diagnostic Tools:
FibroScan®: This non-invasive test measures liver stiffness, providing information about the degree of fibrosis (scarring) present in the liver.
Blood Tests: Specific blood markers can indicate liver function and the severity of cirrhosis.
Management and Treatment:
While cirrhosis is not reversible, effective management can slow its progression and alleviate symptoms:
Lifestyle Changes: If alcohol-related, abstaining from alcohol is crucial. Adopting a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and maintaining a healthy weight can improve liver health.
Medications: Depending on the underlying cause of cirrhosis, medications may be prescribed to manage complications, reduce inflammation, or address specific symptoms.
Regular Monitoring: Routine medical check-ups and follow-up appointments are essential to monitor the progression of cirrhosis and address any emerging issues.
Advanced Interventions: In some cases, advanced treatments such as liver transplantation may be considered for eligible patients with severe cirrhosis.
Prevention:
- Preventing cirrhosis involves addressing its underlying causes and making healthy lifestyle choices:
- Limit alcohol consumption or abstain from it entirely.
- Get vaccinated against hepatitis B.
- Practice safe sex to reduce the risk of hepatitis transmission.
- Maintain a healthy weight and manage conditions like diabetes and high cholesterol.
- Avoid sharing needles or other drug paraphernalia.
Conclusion:
Liver cirrhosis is a serious condition that demands attention, understanding, and early management. As a dedicated ultrasound clinic in London, we are committed to supporting our community’s liver health through advanced imaging techniques and comprehensive care. If you suspect you may be at risk for cirrhosis or are experiencing symptoms, don’t hesitate to contact our clinic for an evaluation. By raising awareness and taking proactive steps to address risk factors, we can collectively work towards preventing and effectively managing cirrhosis. Your liver health is our priority, and we are here to provide the support you