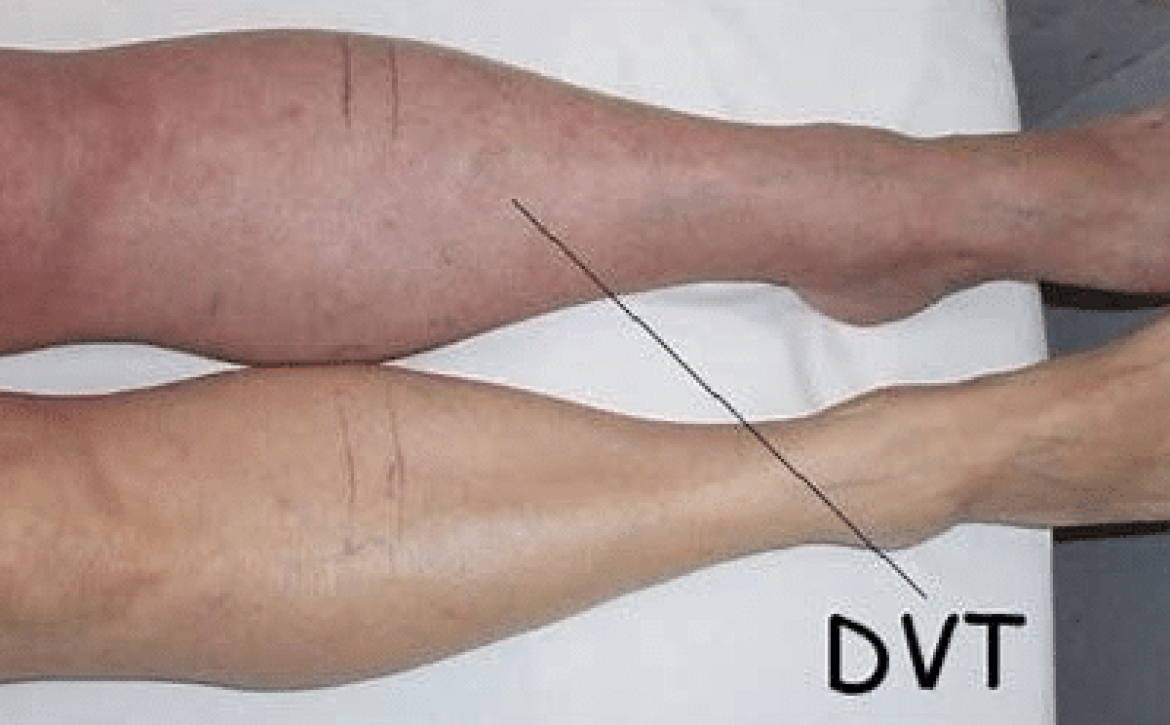
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is a serious medical condition that occurs when a blood clot forms in one of the deep veins within the body, most commonly in the legs. If left undiagnosed and untreated, DVT can lead to potentially life-threatening complications, such as a pulmonary embolism. Thankfully, advancements in medical technology have paved the way for the early detection of DVT using ultrasound, a technique that has proven to be both effective and life-saving.
Understanding Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
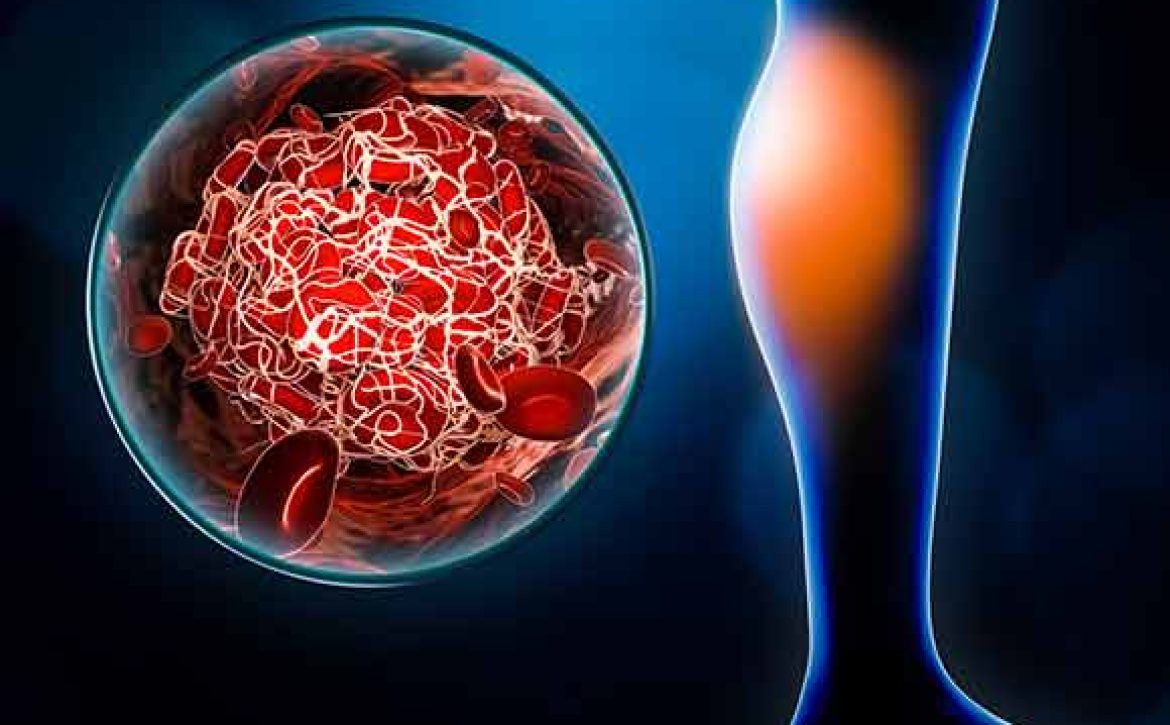
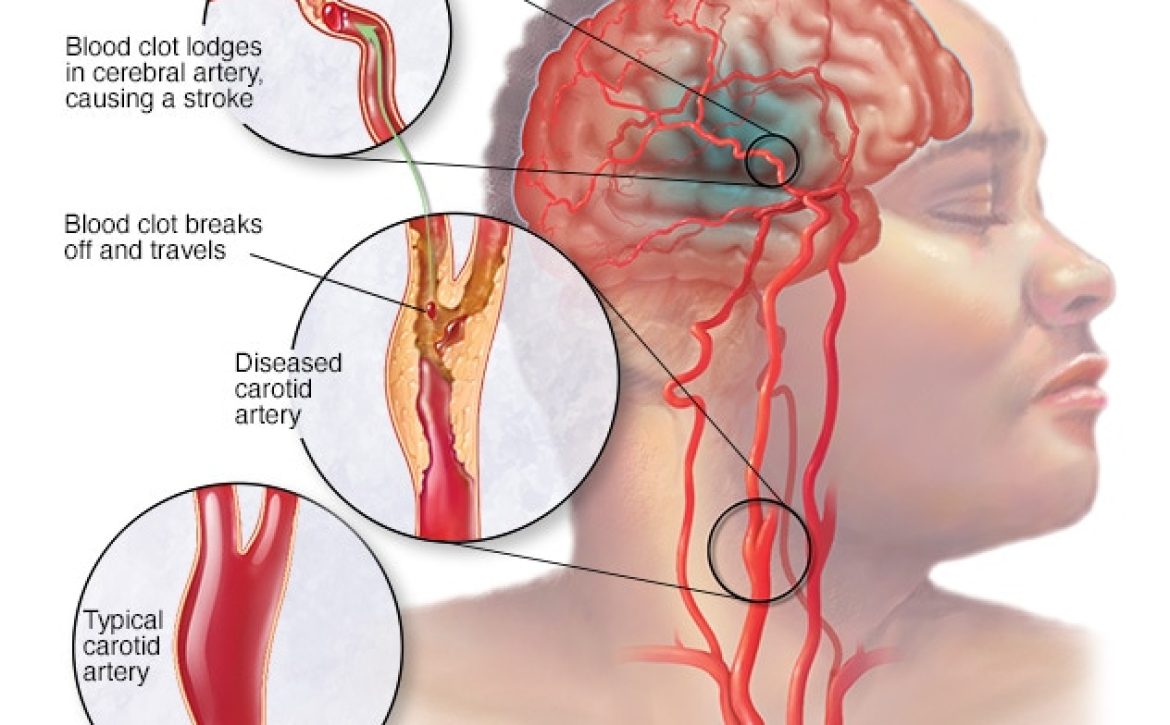
Before we dive into the details of using ultrasound to detect DVT, let’s first understand what DVT is. Deep Vein Thrombosis occurs when a blood clot, also known as a thrombus, forms in the deep veins, usually in the lower legs or thighs. While blood clots are a natural response to prevent excessive bleeding, they can become dangerous when they obstruct blood flow or dislodge and travel to other parts of the body, causing severe complications.
Common risk factors for DVT include prolonged immobility, recent surgery, trauma, obesity, family history, and certain medical conditions. As DVT often presents with minimal or vague symptoms, early detection becomes critical in preventing complications and providing effective treatment.
The Role of Ultrasound in Detecting DVT
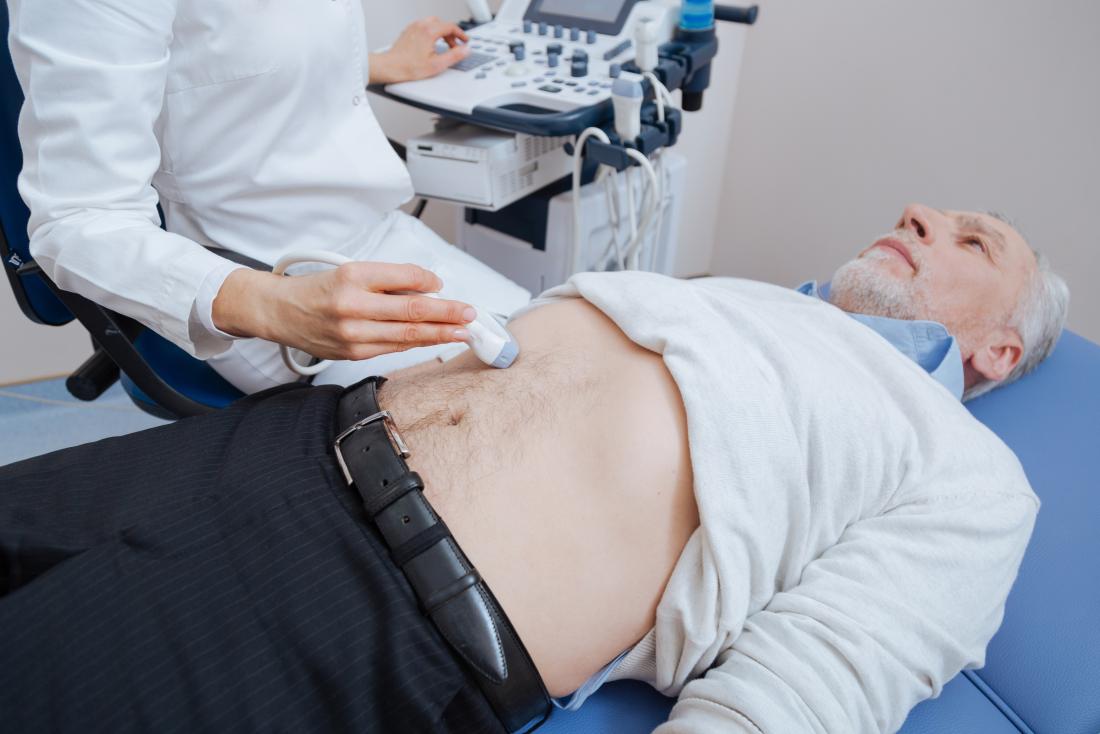
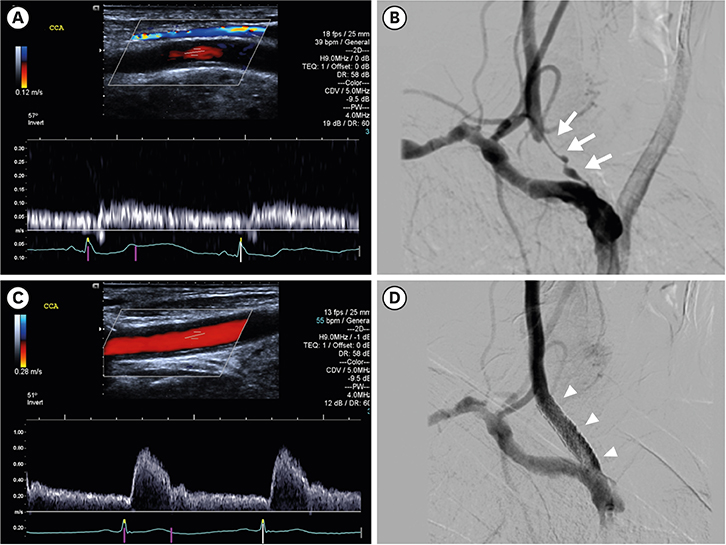
Ultrasound imaging, also known as sonography, utilizes sound waves to produce images of internal body structures. In the case of DVT, ultrasound plays a crucial role in diagnosing and monitoring the condition with its high accuracy and non-invasive nature. This technique allows healthcare professionals to visualize the veins and assess blood flow, enabling them to identify the presence of blood clots and determine their severity.
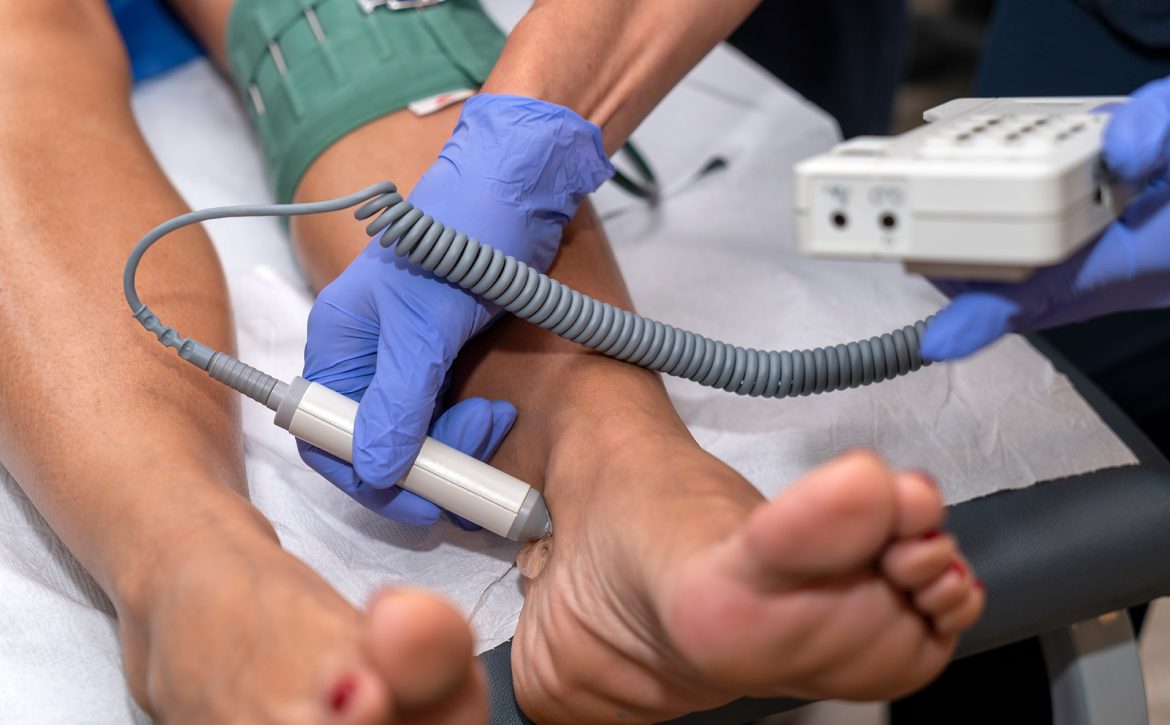
The Procedure: How Ultrasound Detects DVT
During an ultrasound examination for DVT detection, a trained sonographer or healthcare professional applies a gel-like substance on the skin over the affected area. Using a specialized device called a transducer, they then emit high-frequency sound waves that penetrate the tissues and bounce back when they encounter blood vessels. These echoes are converted into real-time images, depicting the blood flow patterns within the veins.
Ultrasound is highly effective in detecting DVT due to its ability to differentiate between normal venous flow and flow obstruction caused by blood clots. By visualizing the veins in real-time, healthcare providers can accurately locate the clot, assess its size, and determine its potential risk for complications, facilitating prompt treatment decisions.
Benefits of Ultrasound in DVT Detection
-
Non-invasive and Painless: Unlike other diagnostic methods, such as venography or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), ultrasound does not involve any radiation exposure or invasive procedures. It is a safe and painless technique, making it suitable for individuals of all ages, including pregnant women.
-
Real-time Imaging: Ultrasound provides real-time images, allowing healthcare providers to evaluate blood flow dynamically. This capability aids in identifying the extent and characteristics of the blood clot, aiding in tailored treatment decisions.
-
Portability and Accessibility: Ultrasound machines are portable and readily available, which enables quick and convenient examinations at various healthcare settings. This accessibility ensures that patients presenting with DVT symptoms can receive timely evaluation.
The Future of DVT Detection: Incorporating Advanced Technologies
While ultrasound has revolutionized the detection of DVT, the medical field continues to evolve, incorporating advanced technologies to enhance accuracy and improve patient outcomes. These advancements include the use of contrast agents to enhance visualization of blood vessels and the integration of artificial intelligence algorithms to aid in the interpretation of ultrasound images, further optimizing the detection process.
Conclusion: Take Action and Spread Awareness
Early detection of Deep Vein Thrombosis can significantly reduce the risk of complications and potentially save lives. Ultrasound has emerged as a invaluable tool in the diagnosis and monitoring of DVT, providing healthcare providers with real-time visualization of blood flow and clot formation. By raising awareness about this lifesaving technique, we can ensure that individuals at risk are promptly evaluated, enabling early intervention and appropriate treatment.