A Guide to Abdomen Ultrasound Scans
Introduction
Modern medical technology continues to evolve, enabling us to peer inside the human body with unprecedented clarity and precision. Abdominal health is a critical component of overall well-being, and diagnostic tools like abdominal ultrasound scans have revolutionized healthcare. In this guide, we’ll explore the world of abdominal ultrasound scans, shedding light on their significance, the procedure, and the wealth of information they offer about our inner workings.
Decoding Abdominal Ultrasound Scans
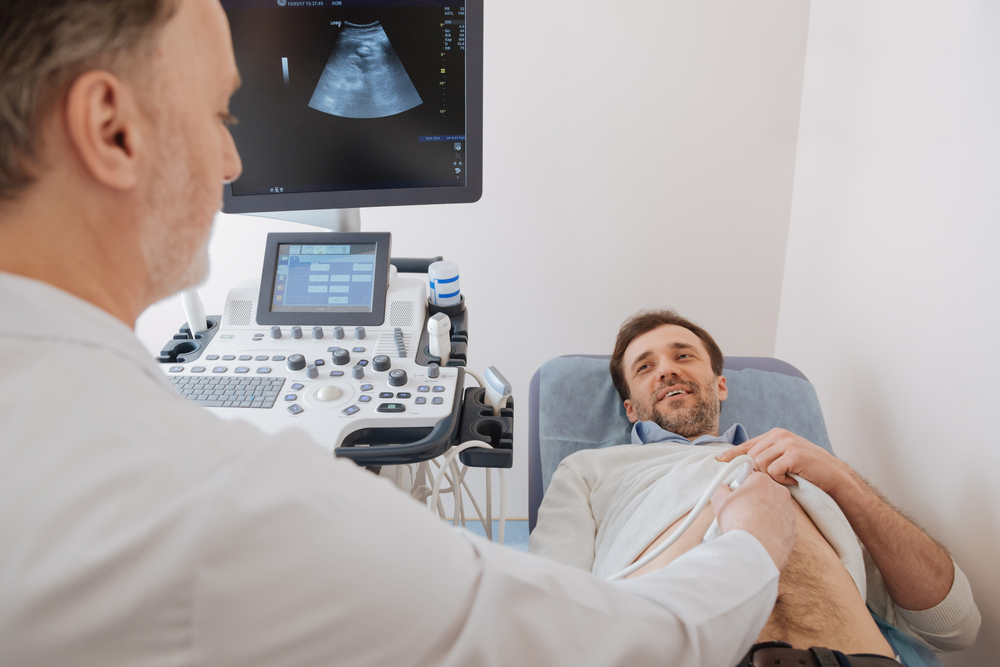
An abdominal ultrasound scan, also known as a sonogram, is a non-invasive imaging technique that employs high-frequency sound waves to capture real-time images of the organs and structures within the abdomen. It provides valuable insights into the health of organs like the liver, kidneys, gallbladder, pancreas, spleen, and more, aiding in the diagnosis and monitoring of a range of medical conditions.
How Abdominal Ultrasound Scans Work
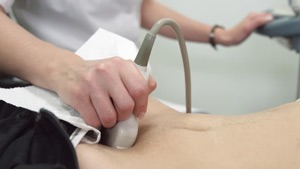
During the procedure, a small handheld device called a transducer is placed on the skin’s surface over the abdominal area. This transducer emits sound waves that travel through the body, and as they encounter different tissues and organs, they bounce back as echoes. The transducer then collects these echoes, and a computer processes the information to create detailed images displayed on a monitor. These images help medical professionals assess the size, shape, and condition of abdominal organs.
Benefits of Abdominal Ultrasound Scans
Non-Invasive and Radiation-Free: One of the primary advantages of abdominal ultrasound scans is that they do not involve radiation exposure. This makes them safe for people of all ages, including pregnant women and children.
Real-Time Imaging: Unlike some imaging techniques that produce static images, ultrasound scans provide real-time images, allowing healthcare providers to observe organ function and movement. This can be especially helpful in assessing blood flow, detecting obstructions, and monitoring dynamic processes.
Diagnosis and Monitoring: abdominal ultrasound scans are instrumental in diagnosing conditions such as liver disease, gallstones, kidney stones, appendicitis, and abdominal masses. They are also used to monitor chronic conditions and assess the effectiveness of treatments.
Guidance for Medical Procedures: abdominal ultrasound scan often play a pivotal role in guiding various medical procedures, such as biopsies, drain insertions, and needle aspirations. The real-time images ensure precision and accuracy during these interventions.
Suitable for Different Populations: Due to their non-invasive nature, abdominal ultrasound scans are ideal for individuals who may have contraindications for other imaging methods, such as those with metal implants or severe claustrophobia.
Preparing for an Abdominal Ultrasound Scan
Preparation for an abdominal ultrasound scan is generally simple. Depending on the specific organs being examined, you may be instructed to fast for several hours before the scan. Fasting helps ensure that the stomach and gallbladder are empty, providing clearer images. Follow any instructions provided by your healthcare provider to ensure the accuracy of the results.
Conclusion
abdominal ultrasound scans offer a glimpse into the intricate world of our internal organs without the need for invasive procedures or exposure to harmful radiation. They empower medical professionals to make accurate diagnoses, monitor ongoing conditions, and guide important medical interventions. Whether you’re experiencing abdominal discomfort, are due for a routine check-up, or require medical assessment, the information provided by an abdominal ultrasound scan can be a crucial step toward maintaining optimal abdominal health. Always consult your healthcare provider for personalized advice and recommendations based on your individual needs.